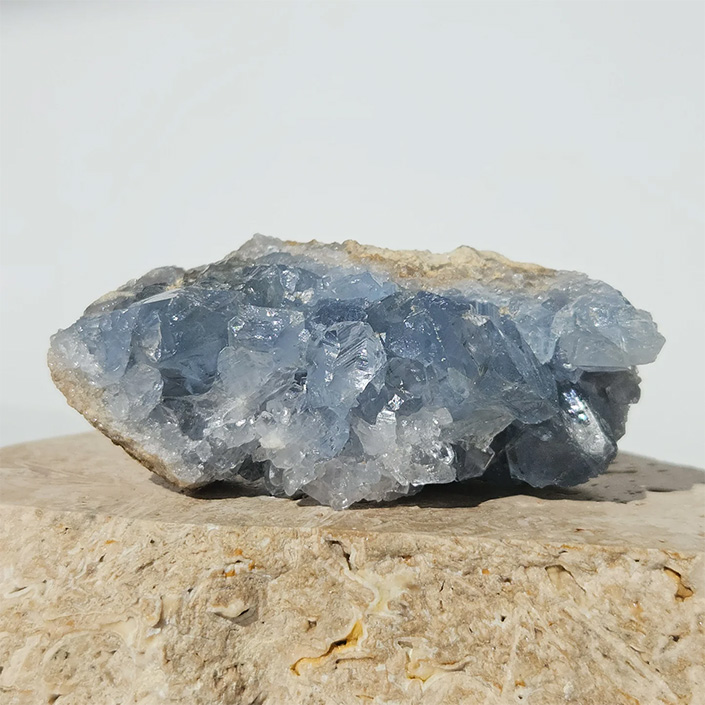
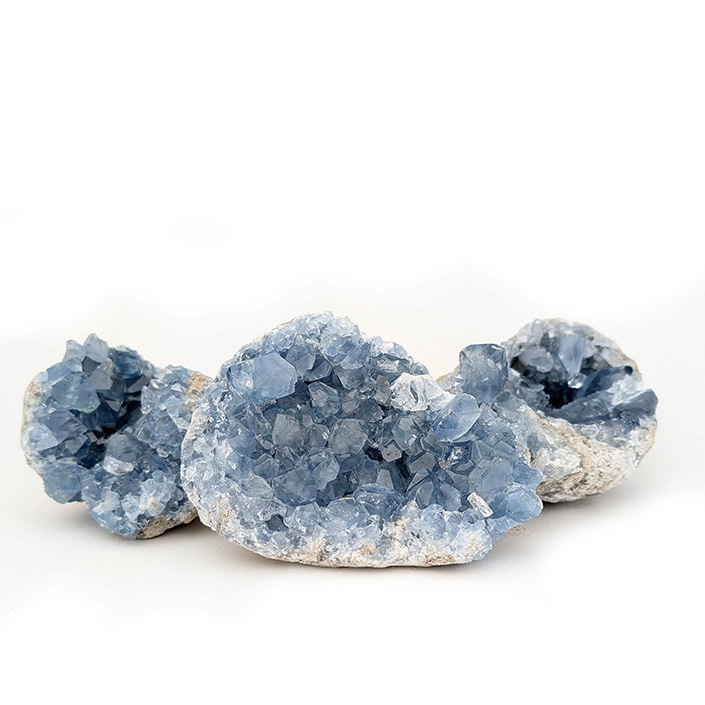
celestine – celestite
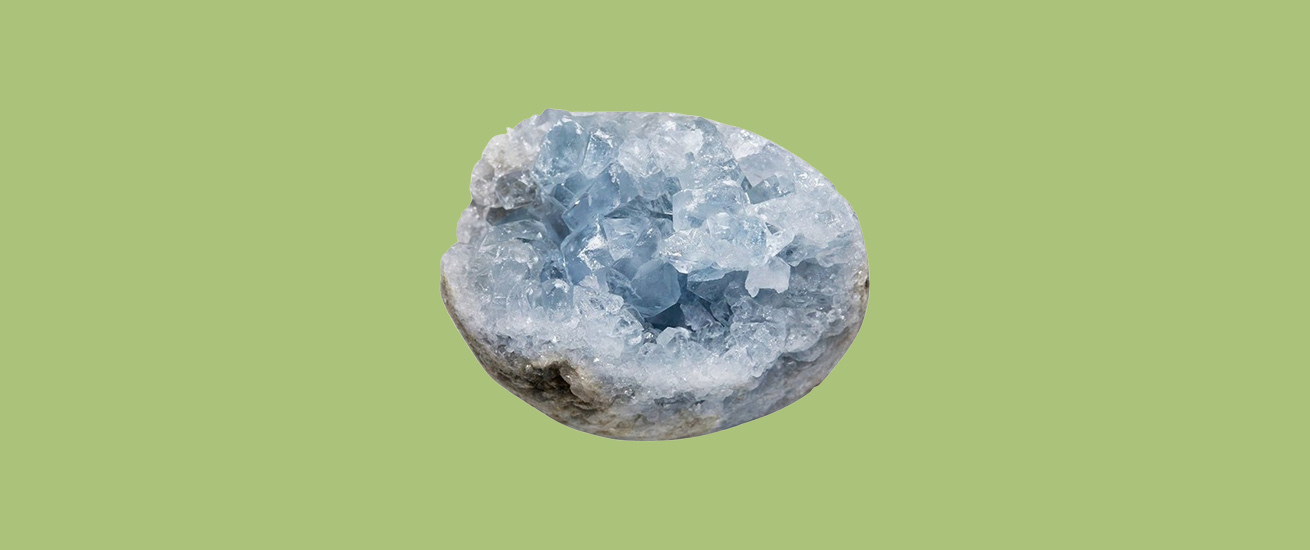
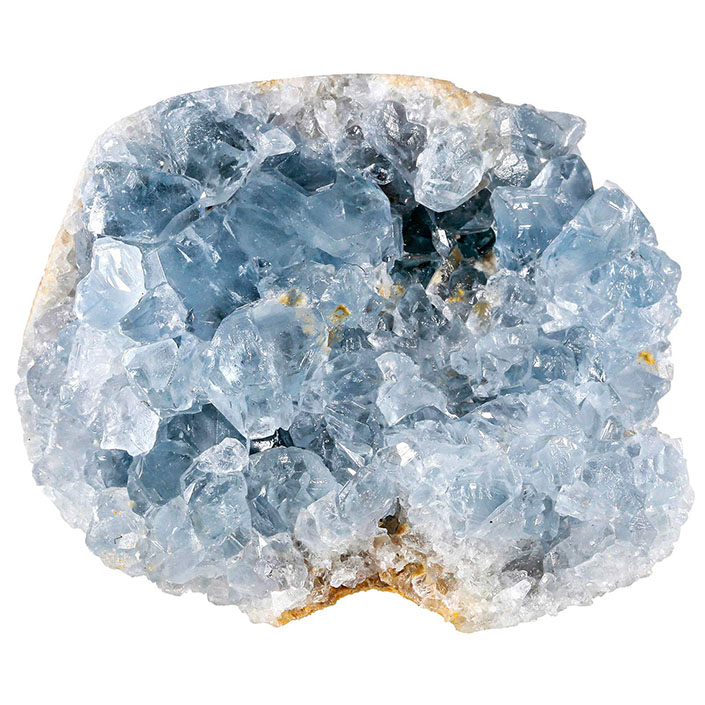
Celestine ore, primarily composed of strontium sulfate (SrSO₄), is an important mineral used in various industrial applications, including the production of strontium carbonate, which is utilized in fireworks, ceramics, and electronics. In Iran, notable deposits of celestine can be found in various regions, including Shahroud and Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province.
Celestine Ore in Shahroud
Shahroud, located in the Semnan Province of Iran, is known for its diverse geological formations and mineral resources. The celestine deposits in this region are typically associated with sedimentary rock formations. These deposits often occur in evaporitic environments, where the conditions favor the precipitation of sulfate minerals.
The celestine ore found in Shahroud is characterized by its crystalline structure and can vary in color from white to light blue or gray. The mining operations in this area focus on extracting celestine for both local use and export. The region’s strategic location near major transportation routes facilitates the distribution of celestine products to various industrial sectors.
Celestine Ore in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province
Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province, located in southwestern Iran, also hosts significant celestine deposits. The geological setting here is more complex, with a mix of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks contributing to the mineral diversity. Celestine in this province is often found in association with limestone and other carbonate rocks, which can influence the quality and extraction methods of the ore.
In this region, celestine mining has gained attention due to the increasing demand for strontium-based products. The local geology provides favorable conditions for the formation of high-purity celestine, making it an attractive resource for both domestic industries and international markets. The province’s rich natural resources, combined with its growing mining infrastructure, position it as a key player in the celestine supply chain.
Conclusion
Both Shahroud and Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province are significant sources of celestine ore in Iran. While Shahroud benefits from its sedimentary rock formations and accessibility, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad offers a more complex geological environment that can yield high-quality celestine. The ongoing exploration and development of these resources are likely to contribute to the growth of Iran’s mining sector and its role in the global mineral market.
Celestine export from Iran
Exporting celestine from Iran to China presents several advantages that can make it an attractive option for both Iranian suppliers and Chinese buyers. Here are some key points highlighting the benefits of Iranian celestine for export to China:
1. High Quality and Purity
Iranian celestine deposits, particularly those in regions like Shahroud and Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province, are known for their high purity levels. This quality is essential for various industrial applications, including the production of strontium carbonate, which is used in fireworks, ceramics, and electronics. High-purity celestine can meet the stringent quality standards required by Chinese manufacturers.
2. Strategic Location
Iran’s geographical position offers a logistical advantage for exporting minerals to China. The proximity of Iranian ports to major shipping routes facilitates efficient transportation, reducing shipping times and costs. This strategic location allows for timely delivery of celestine to Chinese markets, enhancing competitiveness.
3. Growing Demand in China
China is one of the largest consumers of strontium products globally, driven by its extensive manufacturing sector, including ceramics, glass, and electronics. The increasing demand for celestine and strontium carbonate in China creates a significant market opportunity for Iranian exporters.
4. Competitive Pricing
Iranian celestine can often be competitively priced compared to other global suppliers. Factors such as lower production costs, abundant local resources, and favorable exchange rates can contribute to more attractive pricing for Chinese buyers. This competitiveness can help Iranian exporters gain market share in China.
5. Diverse Applications
Celestine is used in various industries, including fireworks manufacturing, where strontium compounds produce vibrant red colors; in the production of ceramics and glass; and in electronics for strontium-based components. The versatility of celestine makes it appealing to a wide range of Chinese industries, further expanding the potential customer base.
6. Established Mining Infrastructure
Iran has developed a robust mining infrastructure that supports the extraction and processing of celestine. This established infrastructure ensures a steady supply of quality ore, reducing the risk of supply disruptions for Chinese buyers.
7. Potential for Long-Term Partnerships
Building trade relationships between Iranian exporters and Chinese manufacturers can lead to long-term partnerships. By establishing trust and reliability in quality and delivery schedules, Iranian suppliers can secure ongoing contracts with Chinese companies, ensuring a consistent market for their products.
8. Supportive Government Policies
The Iranian government has been actively promoting mineral exports as part of its economic diversification strategy. This support may include incentives for mining companies to enhance production capabilities and improve export processes, benefiting both producers and international buyers.
Conclusion
The combination of high-quality celestine, strategic logistics, competitive pricing, and growing demand in China positions Iranian celestine as a strong candidate for export. By leveraging these advantages, Iranian exporters can effectively tap into the lucrative Chinese market while fostering mutually beneficial trade relationships.
Applications of Celestine in Various Industries and Factories (Detailed Explanation)
Celestine, also known as celestite, is a mineral composed of strontium sulfate (SrSO₄). It is distinguished by its characteristic blue color and unique physical and chemical properties, making it valuable in various industries. Below is a detailed explanation of the applications of celestine in different industries and factories:
—
1. **Chemical Industry**
Celestine is the primary source of strontium and is used in the production of various chemical compounds:
– **Production of Strontium Carbonate (SrCO₃):**
– Strontium carbonate is used in the manufacture of specialty glass, ceramics, and pyrotechnic materials.
– It is also utilized in the production of CRT (cathode ray tube) displays and fluorescent lamps.
– **Production of Strontium Nitrate (Sr(NO₃)₂):**
– Strontium nitrate is used in pyrotechnics and flares to produce a bright red flame.
– **Production of Strontium Hydroxide (Sr(OH)₂):**
– Strontium hydroxide is used in sugar refining and the processing of vegetable oils.
—
2. **Electronics Industry**
– **Displays and Lamps:**
– Celestine is used in the production of specialty glass for CRT displays and fluorescent lamps.
– **Semiconductor Materials:**
– Strontium compounds are used in the manufacture of certain semiconductors and electronic components.
—
3. **Ceramic and Glass Industry**
– **Optical Glass:**
– Celestine is used in the production of high-refractive-index glass and specialty optical lenses.
– **Ceramic Glazes:**
– Strontium compounds are used in ceramic glazes to enhance the durability and appearance of ceramic products.
—
4. **Metallurgical Industry**
– **Production of Metal Alloys:**
– Strontium is used in the production of aluminum alloys and other metals to improve mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
– **Metal Refining:**
– Strontium is used as an additive in metal refining processes to remove impurities.
—
5. **Paints and Coatings Industry**
– **Pyrotechnic Colors:**
– Strontium compounds are used to produce red colors in fireworks and flares.
– **Anti-Corrosion Coatings:**
– Strontium compounds are used in industrial coatings to enhance corrosion resistance.
—
6. **Medical Industry**
– **Radiotherapy:**
– Radioactive isotopes of strontium (e.g., Sr-89 and Sr-90) are used in the treatment of bone cancer and to alleviate pain from bone metastases.
– **Medical Diagnostics:**
– Strontium compounds are used as contrast agents in certain medical imaging techniques.
—
7. **Oil and Gas Industry**
– **Drilling Fluids:**
– Celestine is used as an additive in drilling fluids to control density and stabilize oil and gas wells.
—
8. **Agricultural Industry**
– **Chemical Fertilizers:**
– Strontium compounds are used in some chemical fertilizers to improve plant growth and resistance to diseases.
—
9. **Environmental Industry**
– **Water and Wastewater Treatment:**
– Strontium compounds are used in water treatment processes to remove heavy metals and other pollutants.
—
10. **Military and Defense Industry**
– **Flare and Pyrotechnic Materials:**
– Strontium compounds are used to produce red colors in flares and pyrotechnics.
– **Explosive Materials:**
– Strontium compounds are used as additives in certain explosive materials.
—
11. **Research and Scientific Industry**
– **Material Research:**
– Celestine is used in scientific research to study the physical and chemical properties of materials.
– **Advanced Materials Production:**
– Strontium compounds are used in the production of advanced materials such as engineered ceramics and composites.
—
12. **Art and Decorative Industry**
– **Jewelry and Decorative Items:**
– Celestine is used in the production of jewelry and decorative items due to its attractive blue color and transparency.
—
Summary
Celestine, as a source of strontium, is a valuable mineral in various industries. Its primary applications include the production of chemical compounds, electronics, ceramics, glass, medical treatments, and military uses. Due to its unique physical and chemical properties, celestine plays a significant role in both advanced technologies and traditional industries.
Analysis
Celestine (SrSO4)
| Celestine | SiO2 | Al203 | Fe203 | SrSO4 | SrO | SO3 | CaCO3 | CaO | BaO | BaSO4 | MgO |
| N-CS-10 | 2.3 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 93.1 | 53.5 | 40.6 | 1.6 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
MOISTURE DETERMINATION:
Moisture determination was attained for the cargo as bellow:
Moisture (%) = 0.615
SIZE DETERMINATION:
The following size determination were attained for requested sizes was according to our visual estimation/ judgment.
Size breakdown – Approximate Percentage (%)
0 – 10 mm : 05
10 – 300 mm : 95
+300 mm : 0
Total : 100